Cybersecurity in Telecommunications: The Evolving Threat Landscape and How to Safeguard Your Network
In today’s interconnected world, the telecommunications industry forms the backbone of global communication. Whether it’s mobile networks, broadband internet, or the cloud, telecom providers are essential to modern life. However, with this connectivity comes an increased risk of cyber threats. As cyberattacks grow more sophisticated, telecommunications companies are prime targets for a range of malicious actors—from hackers to nation-state adversaries. This post dives deep into the emerging threats and explores key cybersecurity strategies that telecom companies must adopt to protect their critical infrastructures.
1. Why Telecom Networks Are Attractive Targets
Telecom companies are often seen as high-value targets by cybercriminals and hackers due to the sensitive data they handle, including personal communications, financial transactions, and vital business services. A successful attack on a telecom network can have far-reaching consequences, such as disrupting services, stealing customer data, or compromising national security.
Key risks to telecom networks include:
-
Data breaches: Telecom networks store massive amounts of customer data, making them prime targets for data theft.
-
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks: Disrupting network availability can cause significant downtime and affect millions of users.
-
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): State-sponsored attackers often target telecom networks to spy on users, collect intelligence, or sabotage infrastructure.
-
Ransomware attacks: Cybercriminals may lock down network resources or steal sensitive data, demanding ransom for restoration.
2. The Rise of 5G: New Challenges, New Vulnerabilities
The rollout of 5G networks has opened new doors for telecom companies but also introduced new cybersecurity challenges. The sheer volume of connected devices, along with ultra-low latency, makes 5G a prime target for malicious actors.
Cybersecurity concerns associated with 5G include:
-
Expanded attack surface: The increase in connected devices offers more opportunities for attackers to infiltrate networks.
-
Edge computing vulnerabilities: 5G networks often rely on edge computing, which can be harder to secure compared to centralized data centers.
-
Network slicing: The flexibility of 5G networks allows operators to create virtualized networks for specific industries, but these "slices" can introduce vulnerabilities if not properly secured.
3. Strategies for Protecting Telecom Networks
To defend against these evolving threats, telecom companies need a multi-layered security strategy that incorporates both proactive and reactive measures.
Key strategies for cybersecurity in telecom:
-
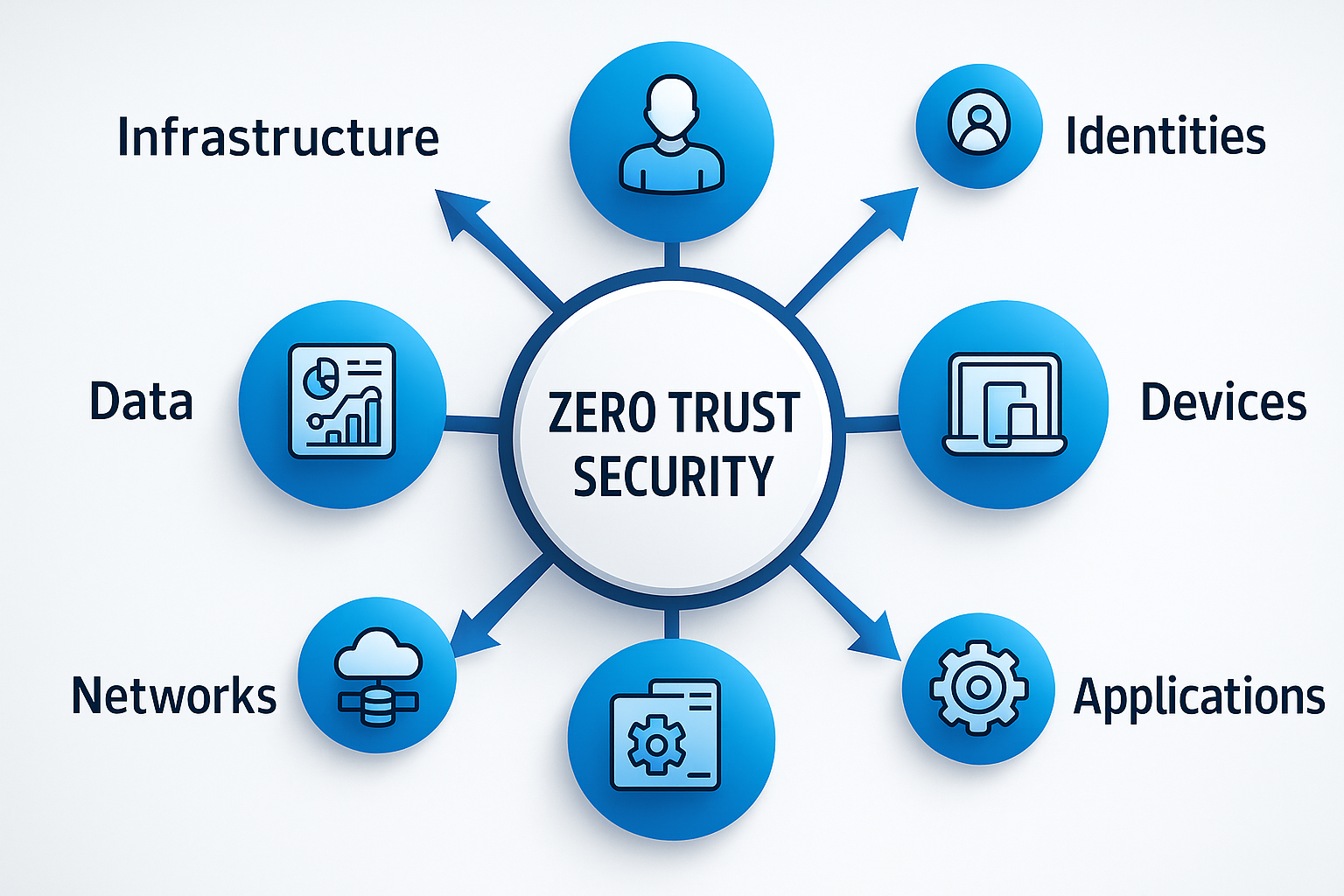
Implement Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA):
Zero Trust is an approach that assumes that both internal and external networks are potentially compromised. By implementing strict access controls and continuously verifying the trustworthiness of devices and users, telecom companies can better protect sensitive data and network resources. -
Regular Penetration Testing and Vulnerability Scanning:
Frequent security testing can help telecom providers identify vulnerabilities before attackers do. Penetration testing, combined with automated vulnerability scans, ensures that all components of the telecom network are secure from potential threats. -
AI and Machine Learning for Threat Detection:
AI and ML technologies can analyze network traffic in real-time to detect unusual behavior and potential threats. These technologies can help identify patterns indicative of cyberattacks and respond quickly to mitigate damage. -
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Encryption:
Telecom companies must secure user access through MFA, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive data. Additionally, encrypting communication data helps to protect against eavesdropping and data theft during transmission. -
Employee Training and Awareness:
The human factor remains one of the weakest links in cybersecurity. Regular employee training on recognizing phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics can greatly reduce the risk of cyberattacks.
4. Compliance with Industry Standards and Regulations
Telecommunications companies must comply with various regulatory frameworks that govern data privacy and cybersecurity. These include:
-
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for protecting European citizens' data.
-
Telecommunications Act and Network and Information Systems (NIS) Directive for UK-based telecom operators.
-
Telecom Regulatory Authority (TRA) guidelines for countries in the Middle East and Africa.
Staying compliant with these standards not only helps to protect data but also reduces the financial and reputational damage from regulatory breaches.
5. The Future of Telecom Cybersecurity
As the telecom industry evolves, cybersecurity must keep pace with new technologies and shifting threat landscapes. Telecom companies will need to embrace a proactive approach to cybersecurity—one that includes continuous monitoring, early detection, and rapid response to emerging threats.
The future of telecom cybersecurity lies in:
-
Automation: Using AI-driven security tools to automate threat detection and response.
-
Blockchain: Leveraging blockchain for secure communication and transaction verification.
-
Collaboration: Sharing threat intelligence among telecom operators and other industries to combat increasingly sophisticated threats.
Conclusion
As the telecommunications industry continues to expand and evolve, the risks associated with cyber threats will only increase. Telecom companies must prioritize cybersecurity, integrating robust defense mechanisms into every aspect of their networks. By staying ahead of emerging threats and adopting cutting-edge technologies, telecom providers can safeguard their infrastructures and ensure the trust of their customers.
For more insights on securing telecom networks and protecting against cyber threats, visit our Cybersecurity Solutions page or get in touch with our experts at NeuralXpert.